How to Save Images in a Vue, Laravel, and S3 Environment
Thank you for your continued support.
This article contains advertisements that help fund our operations.
Table Of Contents
I will write an article focused on saving images to S3 in a Laravel+Vue environment
What is S3
Simple Storage Service.
It is an AWS storage service.
It is specialized for storing files, and the basic understanding is that you can just dump files here.
Environment
Laravel 6
Vue 2
Commands
Commands for Laravel.
composer require league/flysystem-aws-s3-v3 "~1.0"This command installs the package.
If you encounter errors in package dependencies, run:
composer update⇨ How to deal with issues when the composer require command fails miserably with versions
Creating Vue Display
<template>
<div>
// When an image is selected, the function is triggered, and the image data is stored in 'image'
<input
type="file"
accept="image/jpeg, image/png"
@change="onChangeImage"
/>
<button @click="postImage">Submit</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
image: {}
};
},
methods: {
// Stores image data
onChangeImage: function(e) {
this.image = e.target.files[0];
},
// Posts to Laravel
postImage: function() {
// Header information for sending the image
const config = {
header: {
"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data"
}
};
// When sending an image, use FormData
var formData = new FormData();
// The first argument of append is the key, and the second argument is the data
formData.append("image", this.image);
// If you want to include text or other items
// formData.append("text", this.text);
axios.post("/post/s3/image", formData, config).then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
}
}
};
</script>This is the minimum necessary code for sending images.
When sending text or other items, simply append them in the same way.
Setting up AWS
①Creating S3
Go to the management console and select S3.
Click on "Create Bucket"
⇨ Bucket Name: "laravel-test-s3"
⇨ Region: "Tokyo Region"
Keep the rest as defaults and click on create bucket.
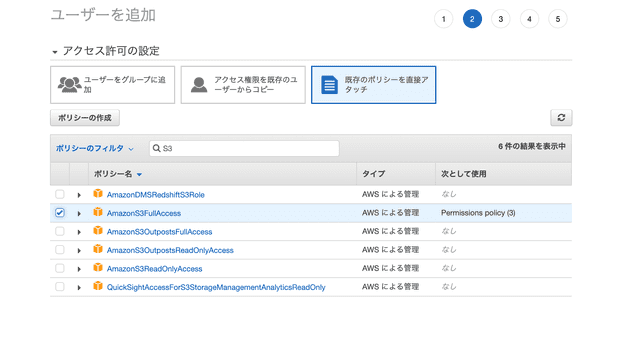
②Creating IAM
Click on "Add User"
⇨ User name: "laravel-test-s3"
⇨ Access type: "Programmatic access"
⇨ Access permissions
⇨ Choose existing policies
⇨ (Search for S3) AmazonS3FullAccess
⇨ Create the user with default settings
⇨ Download the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key in CSV format
Creating Laravel Code
①Modify the .env file
In the initial state of a Laravel project, there are entries around line 36 in the .env file where you will write the following:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=AccessKeyIDDownloadedEarlier
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=AccessKeySecretFromDownloadedCSV
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=ap-northeast-1
AWS_BUCKET=laravel-test-s3If you are using the Tokyo region, the AWS_DEFAULT_REGION should be "ap-northeast-1".
If your bucket name is different from the one in this article, please modify it accordingly.
Reflect the changes to the env file (cache) with the following command:
php artisan config:cache②Modify the Controller
Create a PostImageController.php and add the following code:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Storage;
class PostImageController extends Controller
{
public function s3(Request $request)
{
// For readability, define the disk in advance
$disk = Storage::disk('s3');
// The posted image
$image = $request->image;
// putFile saves the image and returns the saved path (below the bucket), the third argument is whether it will be public or private
$path = $disk->putFile('images', $image, 'public');
// $path contains the saved path
// You can retrieve it by saving $path to a database column
return response()->json(['response' => $path], 200);
}
}That's it, you can now save images.
Check from the management console.
Also, the $path variable contains the saved path, so you can save it to a database column for retrieval.
Conclusion
That concludes the process of sending images from Vue to Laravel and saving them to S3.
Were you able to successfully save the images?
For feedback or complaints regarding the article, please DM me on Twitter. Thank you and goodbye!
Popular Articles
Deploying a PHP 7.4 + Laravel 6 Project to AWS EC2
Other S3 Articles
【Laravel + S3】How to save user-defined metadata at the time of saving