How to Implement Follow Functionality in Laravel (jQuery, Vue.js Support)
Thank you for your continued support.
This article contains advertisements that help fund our operations.
Table Of Contents
- Implementation Environment
- Prerequisites
- Implementation Specifications
- Database Design
- Create a Database Migration File
- Create the Skeleton of the User List Page
- Define a Many-to-Many Relationship in the Model
- Create an API for Following
- Triggering the API from the View
- Implementing with axios in Vue.js
- Dealing with Errors
- Creating an API to Unfollow Users
- Additional Notes
- Conclusion
I wrote an article about how to implement follow functionality in Laravel with support for jQuery and Vue.js. The implementation is done through asynchronous communication (Ajax).
Implementation Environment
Laravel Framework 8.*
Laravel Mix v6.0.*Prerequisites
Authentication functionality for users is in place.
Implementation Specifications
To be implemented on the user list page.
Next to the user's name, there is a follow button that allows users to follow each other.
Users can also unfollow each other.
CSS styling will be omitted.
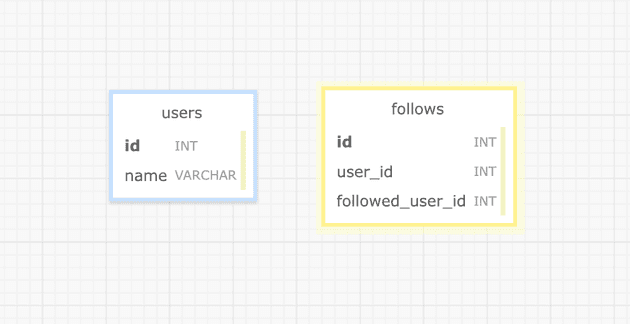
Database Design
The column names are a bit difficult to name, but:
user_id represents the user who is following
followed_user_id represents the user being followed
Create a Database Migration File
※ The users table will be omitted (in most cases, it already exists)
Creating the follows table
Run the command:
php artisan make:migration create_follows_tableA file will be created at:
databases/migrations/2022_12_29_075711_create_follows_table.phpEdit the created migration file
public function up()
{
Schema::create('follows', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->bigInteger('user_id');
$table->bigInteger('followed_user_id');
$table->timestamps();
});
}Create the table using the command
php artisan migrateIf successful, you should see the following message:
php artisan migrate
Migrating: 2022_12_29_075711_create_follows_table
Migrated: 2022_12_29_075711_create_follows_table (26.20ms)Create the Skeleton of the User List Page
web.php
use App\Http\Controllers\UserController;
Route::get('/users', [ UserController::class, 'index']);Create the controller using the command
php artisan make:controller UserControllerEdit the controller
App\Http\Controllers\UserController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\User;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$users = User::all();
return view('user/index',compact('users'));
}
}
Create the view file
Create a file at:
resources/views/user/index.blade.phpEdit index.blade.php
Include only the necessary markup:
@foreach($users as $user)
<div>
<div>{{$user->name}}</div>
<button>Follow</button>
</div>
@endforeachIf there is user data, it will be displayed as shown in the image.
If you are unsure how to insert test data for users, read this article on how to prepare test data in Laravel using Seeders.
Laravel: How to Prepare Test Data (Using Seeder)
The skeleton is now completed
Next, we will start writing the actual code for the follow functionality.
Define a Many-to-Many Relationship in the Model
We will define a many-to-many relationship between the User model and the Follow model.
Create the Follow model
Run the command:
php artisan make:model FollowThis will create app/Models/Follow.php.
Define the relationship in the User model
App/Models/User.php
public function follows()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\User','follows','user_id','followed_user_id');
}Since the naming convention does not allow for the standard implementation of the follows table as the intermediate table, this is how it is implemented.
If you are unsure about this part, read the following article for more information.
Laravel: How to Save and Display Many-to-Many Relationships (belongsToMany)
Create an API for Following
Create the FollowController
Run the command:
php artisan make:controller FollowControllerEdit web.php
use App\Http\Controllers\FollowController;
Route::group(['middleware' => 'auth'], function () {
Route::post('/follow/{userId}', [ FollowController::class, 'store']);
});Edit FollowController.php
Edit App\Http\Controllers\FollowController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Auth;
class FollowController extends Controller
{
public function store($userId)
{
Auth::user()->follows()->attach($userId);
return;
}
}The API is now complete.
Triggering the API from the View
resouces/views/user/index.blade.php
This file was edited to display the user list earlier, but this time we will write everything here. Feel free to create a separate JavaScript file as needed.
<!-- This is essential to avoid errors -->
<!-- It is usually included in layouts/app.blade.php -->
<meta name="csrf-token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}" />
@foreach($users as $user)
<div>
<div>{{$user->name}}</div>
<button onclick="follow({{ $user->id }})">Follow</button>
</div>
@endforeach
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
function follow(userId) {
$.ajax({
// Include this to prevent a 419 error
headers: { "X-CSRF-TOKEN": $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr("content") },
url: `/follow/${userId}`,
type: "POST",
})
.done(data => {
console.log(data)
})
.fail(data => {
console.log(data)
})
}
</script>Success is indicated by no errors when the button is pressed and data is inserted into the database table.
This concludes the follow functionality.
Resolving "Laravel: $ is not defined" Error
Implementing with axios in Vue.js
<template>
<div v-for="user in users">
<div>{{ user.name }}</div>
<button @click="follow(user.id)">Follow</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
follow(userId) {
axios
.post(`/follow/${userId}`)
.then(({ data }) => {})
.catch(err => {})
},
},
}
</script>Triggering a POST request to the same URL as in Ajax will make it work.
If you encounter errors related to csrf, read the following article.
Resolving CSRF Token Error in Laravel and Vue.js with axios
Dealing with Errors
What if I get a 401 error?
It may be due to not being logged in.
Make sure to implement user authentication and log in.
Resolving Laravel 401 Error When Unable to Perform POST Requests or Access
What if I get a 419 error?
The csrf token is not being sent.
Review the view section carefully.
Resolving Laravel 419 Error - When POST Requests Fail
What if I get a 500 error?
There could be various reasons.
Open storage/logs/laravel.log, review the error logs, and investigate based on the error reported.
Creating an API to Unfollow Users
web.php
Route::group(['middleware' => 'auth'], function () {
Route::post('/follow/{userId}', [ FollowController::class, 'store']);
// Add the following route
Route::post('/follow/{userId}/destroy', [ FollowController::class, 'destroy']);
});FollowController.php
public function destroy($userId)
{
Auth::user()->follows()->detach($userId);
return;
}To unfollow a user, simply make a POST request to the following URL:
/follow/<<User ID>>/destroyAdditional Notes
If you prefer a more advanced approach (e.g., writing logic in the model), you can refer to the following article:
Implementing 'Like' Functionality in Laravel
Conclusion
That's it for now.
I know it was a bit lengthy and challenging, but I hope it can be helpful to someone.
This blog is supported by ad clicks. Thank you for your support.
Until next time!
Popular Articles
Deploying a PHP7.4 + Laravel6 Project to AWS EC2
Implementing Breadcrumbs in Laravel with laravel-breadcrumbs