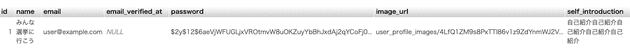How to Create a Profile Editing Feature in Laravel
Thank you for your continued support.
This article contains advertisements that help fund our operations.
Table Of Contents
A guide on how to create a profile editing feature in Laravel
Adding Columns to the Users Table
If Your Application is Not in Production
If you are working in a development environment, you can modify an existing migration file.
If you prefer to store the information in a separate table, you can create a new table and set up a relationship. However, in this guide, we will proceed by adding new columns to the existing users table.
database/migrations/0001_01_01_000000_create_users_table.php
Schema::create('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->timestamp('email_verified_at')->nullable();
$table->string('password');
$table->string('image_url')->nullable(); // Added
$table->string('self_introduction',2000)->nullable(); // Added
$table->rememberToken();
$table->timestamps();
});We added two columns for storing profile images and self-introductions.
Run the following command to apply the changes to the database. Note that this will remove any existing test data, so make sure to use factories and seeders to generate test data programmatically.
php artisan migrate:fresh --seedHow to Create Test Data Using Laravel Factories
If Your Application is in Production
If your application is already running in production, you cannot modify existing migration files.
Since migration files retain their execution history, any changes made to an already executed file will not take effect. Instead, you need to create a new migration file.
Generate a new migration file using the following command:
php artisan make:migration add_image_url_to_users_tableThis will create a file named database/migrations/0001_01_01_000000_add_image_url_to_users_table.php, where you can add the following code:
public function up(): void
{
Schema::table('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->string('self_introduction',2000)->nullable()->after('password'); // Added
$table->string('image_url')->nullable()->after('password'); // Added
});
}
public function down(): void
{
Schema::table('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->dropColumn('image_url'); // Added
$table->dropColumn('self_introduction'); // Added
});
}Run the following command to apply the migration:
php artisan migrateHow to Improve Readability of Laravel Migrations with After Clauses
Creating Routes
We need two routes: one for the profile edit page and another for handling updates.
routes/web.php
use App\Http\Controllers\ProfileController;
Route::get('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'edit'])->name('profile.edit');
Route::patch('/profile', [ProfileController::class, 'update'])->name('profile.update');Creating the Controller
Generate a new controller using the following command:
php artisan make:controller ProfileController
php artisan storage:linkWrite the following code in the generated controller:
app/Http/Controllers/ProfileController.php
use App\Http\Requests\ProfileUpdateRequest; // Added use statement
~~
// Edit page
public function edit(Request $request)
{
return view('profile.edit', ['user' => $request->user()]);
}
// Update profile
public function update(ProfileUpdateRequest $request)
{
$user = $request->user();
$user->name = $request->name;
$user->self_introduction = $request->self_introduction;
$image = $request->file('image');
if($image){
$image_url = Storage::disk('public')->put('user_profile_image', $image, 'public');
$user->image_url = $image_url;
}
if($user->isDirty()){
$user->save();
}
return redirect()->route('profile.edit')->with('status', 'profile-updated');
}How to Store Images with Vue, Laravel, and S3
Creating Validation Rules
Generate a request class for validation:
php artisan make:request ProfileUpdateRequestapp/Http/Requests/ProfileUpdateRequest.php
public function rules(): array
{
return [
'name' => ['required', 'string', 'max:255'],
'image' => ['nullable','image','mimes:jpeg,jpg,png','max:10000'],
'self_introduction' => ['nullable','string','max:2000']
];
}This request class is used in the controller as follows:
use App\Http\Requests\ProfileUpdateRequest; // Added use statement
public function update(ProfileUpdateRequest $request)Beginner’s Guide to Laravel Form Request Validation
Creating the View
Create the file resources/views/profile/edit.blade.php with the following content:
<form
method="post"
action="{{ route('profile.update') }}"
class="mt-6 space-y-6"
enctype="multipart/form-data"
>
@csrf
<div>
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input
id="name"
name="name"
type="text"
class="mt-1 block w-full"
value="{{ old('name', $user->name) }}"
required
autofocus
autocomplete="name"
/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="image">Image</label>
<input id="image" type="file" name="image" class="mt-1 block w-full" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="self_introduction">Self Introduction</label>
<textarea
id="self_introduction"
name="self_introduction"
class="mt-1 block w-full"
>
{{ old('self_introduction', $user->self_introduction) }}</textarea
>
</div>
<div class="flex items-center gap-4">
<button>Save</button>
</div>
</form>Confirming Profile Save
It looks like the profile was successfully saved.
Images are stored in /storage/app/public/user_profile_image.
Displaying the Image
You can display the saved profile image using the following path:
<img src="{{ asset('storage/'.$user->image_url) }}" />Conclusion
This guide covered how to implement a profile editing feature in Laravel.
Although it's not common to store images in Laravel’s local storage, it can be useful for prototyping before moving to cloud storage like S3.
If you plan to eventually migrate to S3, you might want to store image_url with a /storage prefix from the start:
<img src="{{ $user->image_url }}" />This way, you won't need to modify the frontend later.
I hope this guide helps!